Tri 2 MCQ Reflection
AP Classroom MCQ Final Tri 2 Corrections
Score
45/50
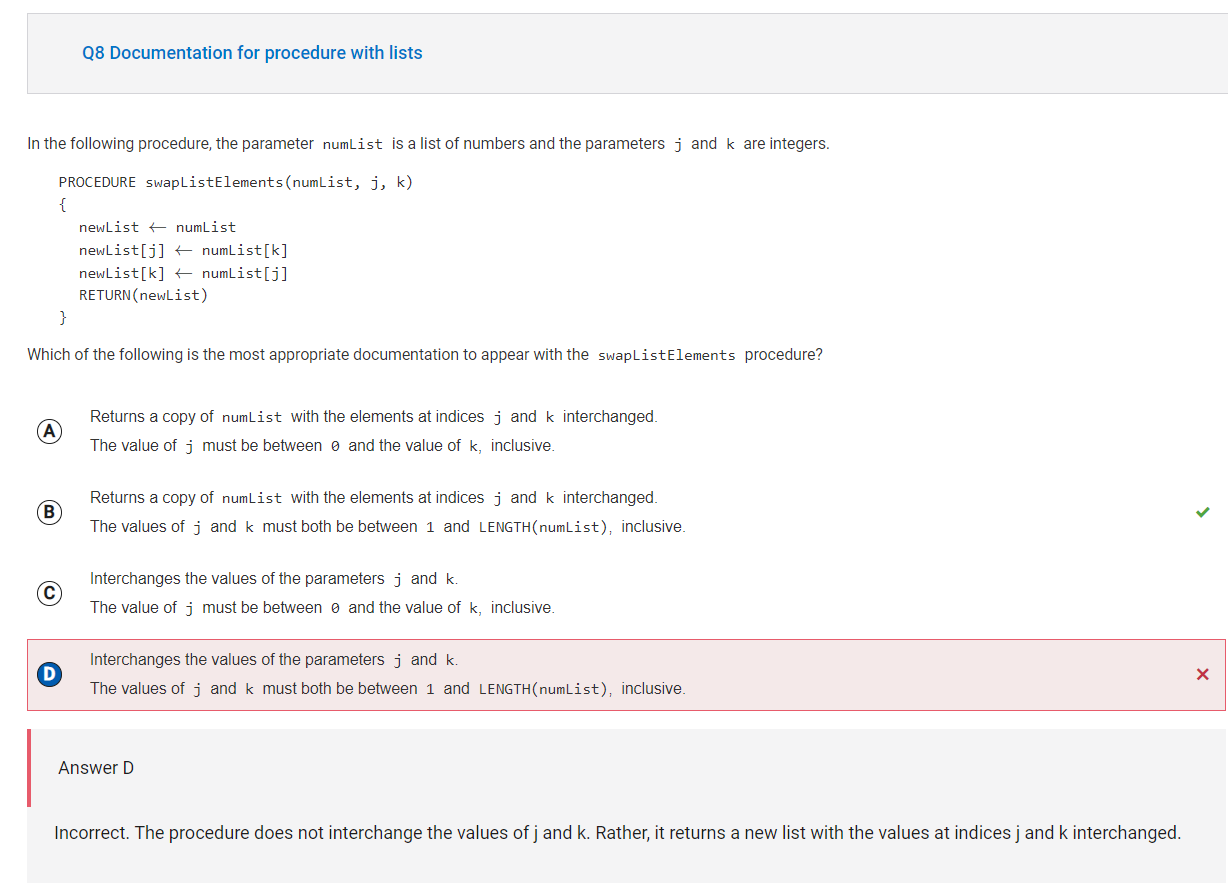 The procedure creates a copy of numList called newList. The element at
The procedure creates a copy of numList called newList. The element at newList[j] is assigned the element at numList[k], and the element at newList[k] is assigned the element at numList[j]. Therefore, the difference between numList and newList is that the elements at indices j and k are interchanged. The procedure only works if j and k are valid list indices, so it is important to document that j and k are both between 1 and LENGTH(numList), inclusive.
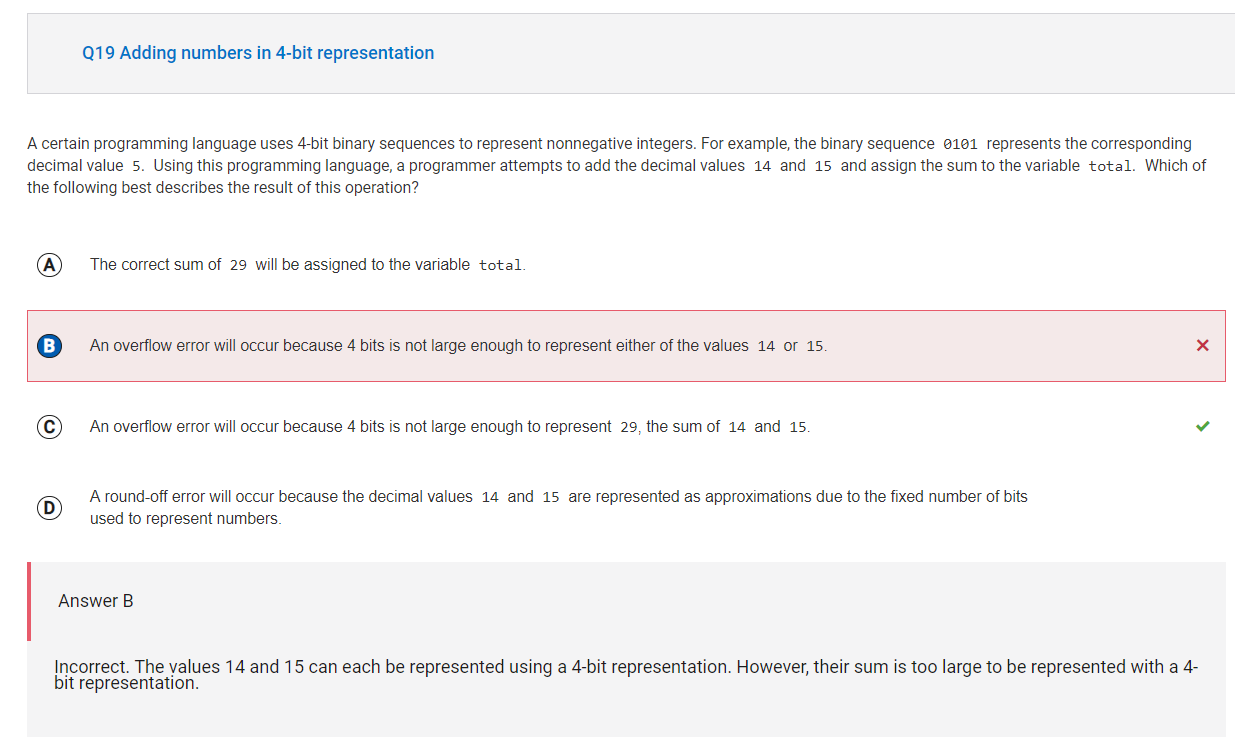 The largest binary value that can be represented using 4 bits is 1111, which is equal to the decimal value 15. Since the sum is larger than the largest representable value, an overflow error will occur.
The largest binary value that can be represented using 4 bits is 1111, which is equal to the decimal value 15. Since the sum is larger than the largest representable value, an overflow error will occur.
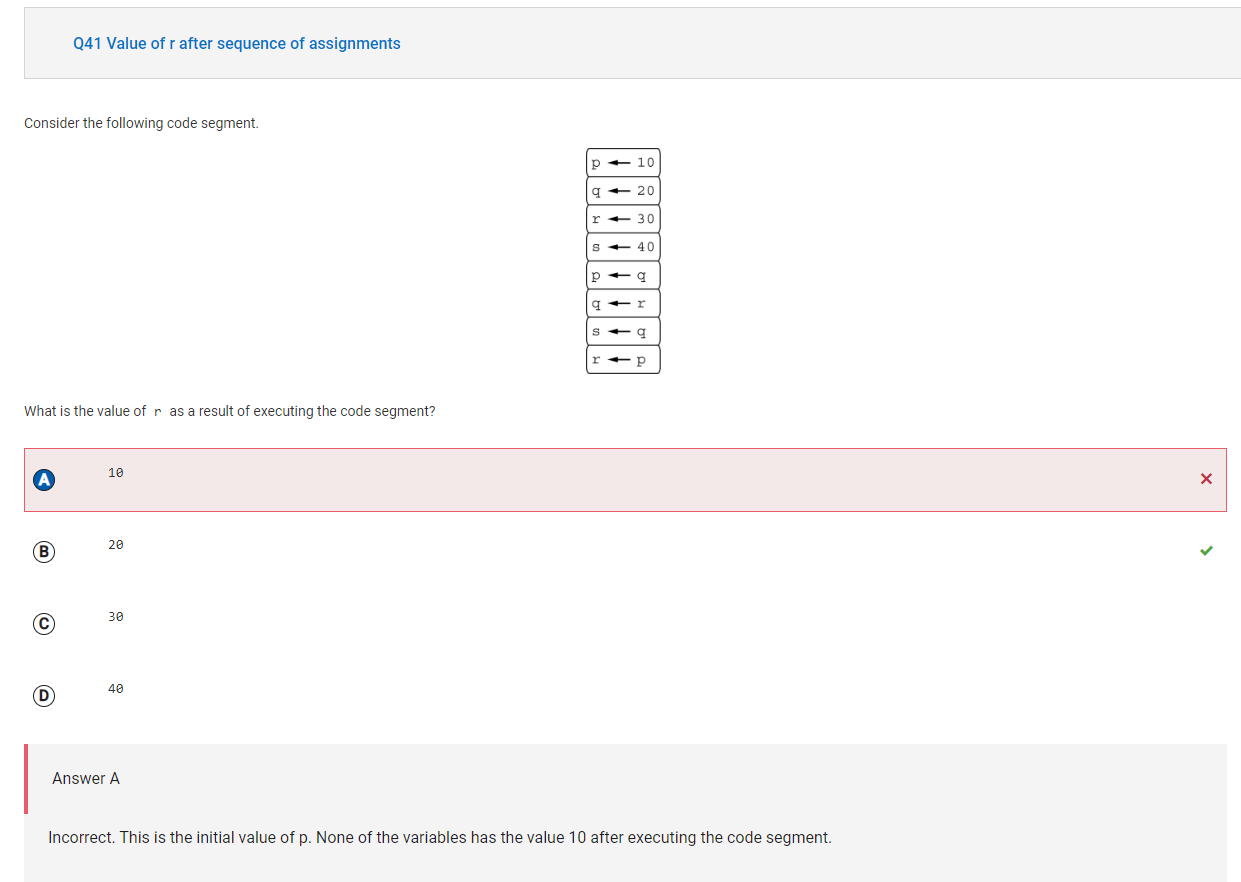 The first four statements assign values to the variables. The fifth statement assigns the value of q (which is 20) to p. The sixth statement assigns the value of r (which is 30) to q. The seventh statement assigns the value of q (which is 30) to s. The last statement assigns the value of p (which is 20) to r. Therefore, r has the value 20. After executing the code segment, the value of p is 20, the value of q is 30, the value of r is 20, and the value of s is 30.
The first four statements assign values to the variables. The fifth statement assigns the value of q (which is 20) to p. The sixth statement assigns the value of r (which is 30) to q. The seventh statement assigns the value of q (which is 30) to s. The last statement assigns the value of p (which is 20) to r. Therefore, r has the value 20. After executing the code segment, the value of p is 20, the value of q is 30, the value of r is 20, and the value of s is 30.
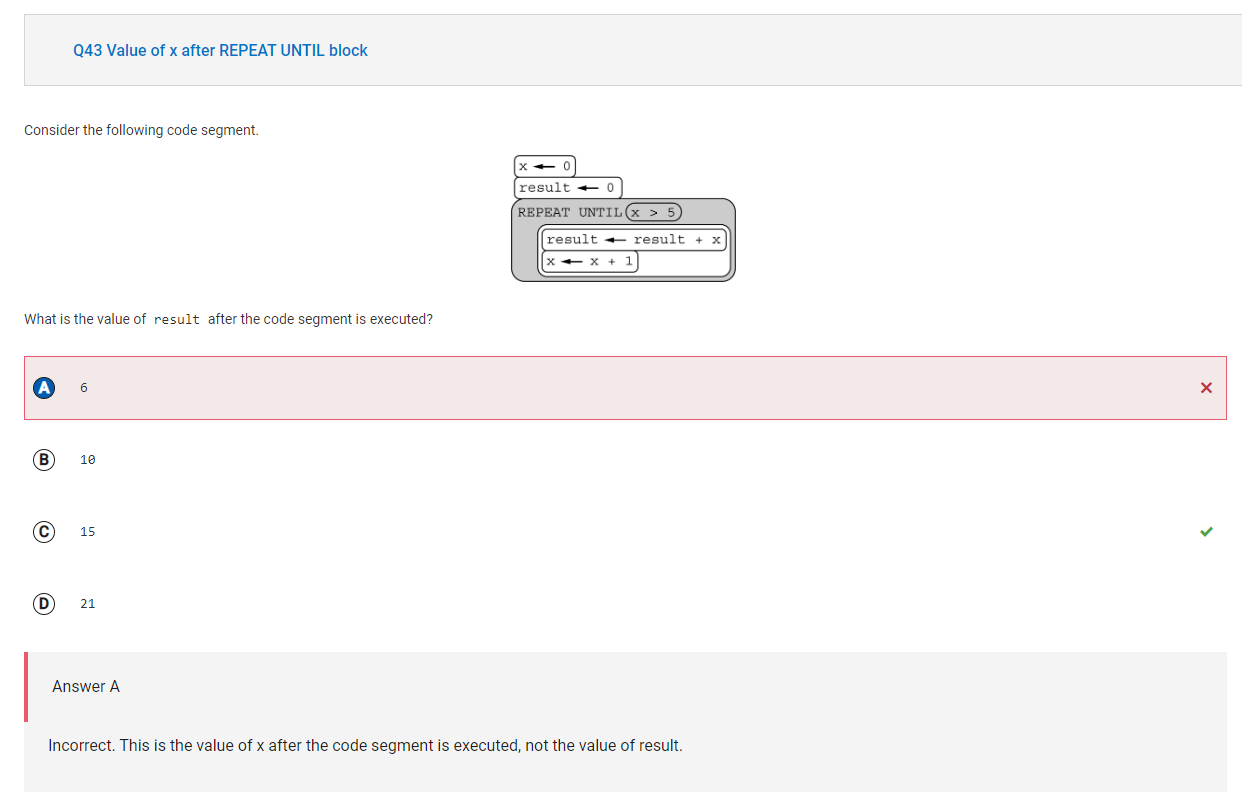 The variables x and result are initialized to 0. Inside the loop, result is increased by x and x is increased by 1. The loop terminates when x exceeds 5. Therefore, result is assigned the sum of the integers from 0 to 5, or 15.
The variables x and result are initialized to 0. Inside the loop, result is increased by x and x is increased by 1. The loop terminates when x exceeds 5. Therefore, result is assigned the sum of the integers from 0 to 5, or 15.
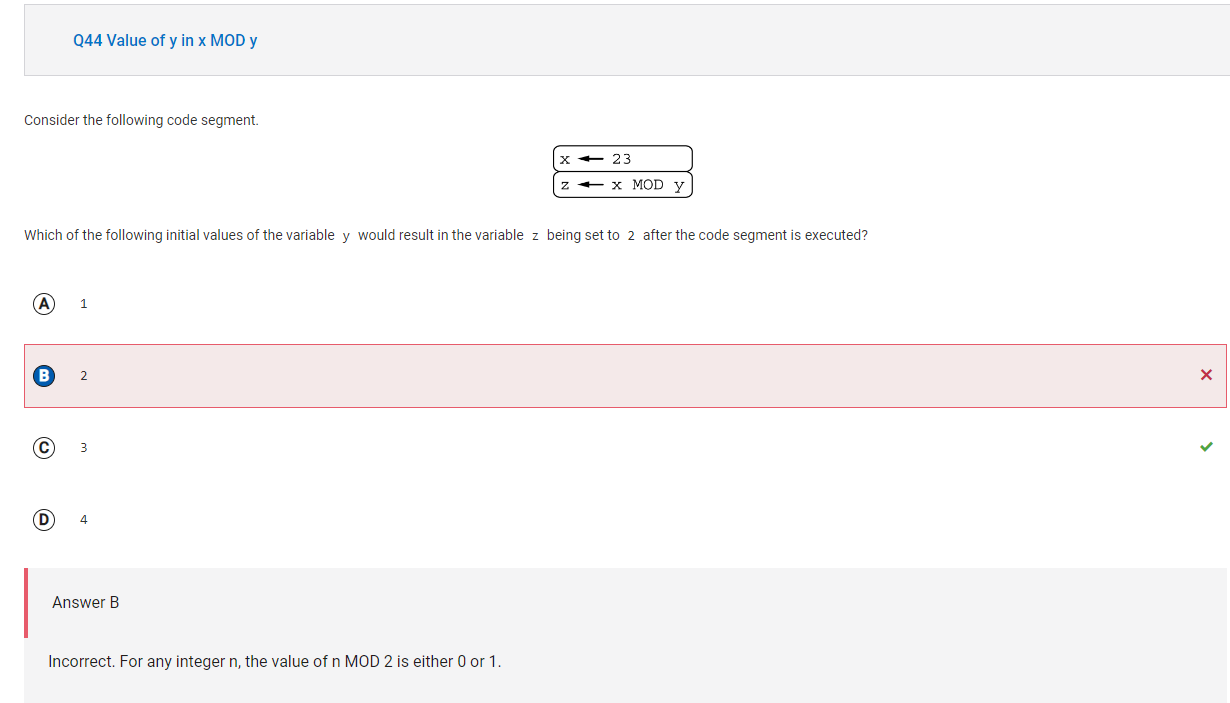 The remainder when 23 is divided by 3 is 2, so 23 MOD 3 is equal to 2.
The remainder when 23 is divided by 3 is 2, so 23 MOD 3 is equal to 2.